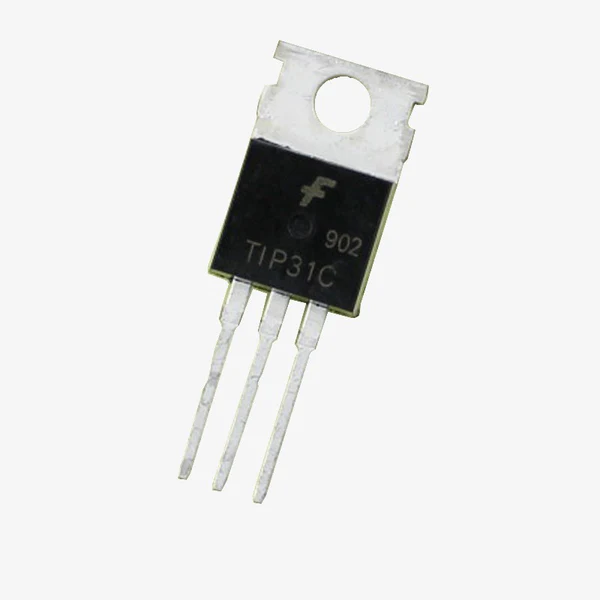
The TIP31 is an NPN bipolar junction transistor (BJT) but it falls under the category of power transistors. This means it’s designed for applications that require handling larger currents compared to small signal transistors like the BC547 or MPSA06
Here’s a breakdown of the TIP31’s key features and how it compares to the other transistors:
TIP31 NPN Power Transistor:
- Package: Typically TO-220 (larger through-hole package for better heat dissipation)
- Applications:
- Driving motors (DC motors, stepper motors)
- Power switching (e.g., controlling relays, solenoids)
- Audio amplifier circuits (low-frequency)
Advantages of TIP31:
- High Current Handling: Can handle significantly higher collector currents compared to BC547 or MPSA06 (typically in the range of amperes).
- Relatively High Voltage Rating: Can withstand higher voltages between collector and emitter compared to small signal transistors.
Things to Consider:
- Lower Current Gain: TIP31 has a lower current gain (hFE) compared to small signal transistors. It’s not ideal for applications requiring high voltage amplification.
- Heat Dissipation: Due to higher power handling, TIP31 might require a heat sink to dissipate heat effectively depending on the application and current levels.
- Control Current: While it can handle high collector currents, the base current required to control the TIP31 can also be higher compared to small signal transistors. You might need to use a driver circuit to provide sufficient base current.
Choosing Between TIP31, BC547, and MPSA06:
- If your project involves controlling motors, relays, or requires power switching of moderate to high currents, the TIP31 is a suitable choice.
- For applications requiring low-power amplification or simple switching with low currents, the BC547 or MPSA06 are better options.
Using TIP31 in Your Project:
Due to its power handling capabilities, using the TIP31 might involve additional considerations:
- Heat sink: Depending on the current and power dissipation, a heat sink might be necessary to prevent the transistor from overheating.
- Base Current Drive: You might need to use a driver circuit (e.g., another transistor or integrated circuit) to provide sufficient base current to control the TIP31 effectively.
- Flyback diode: When driving inductive loads like motors, a flyback diode might be necessary to protect the transistor from voltage spikes.
Always consult the TIP31 datasheet for detailed specifications, pinout information, and circuit examples specific to power transistor applications.
You must be logged in to post a review.



















Reviews
There are no reviews yet.