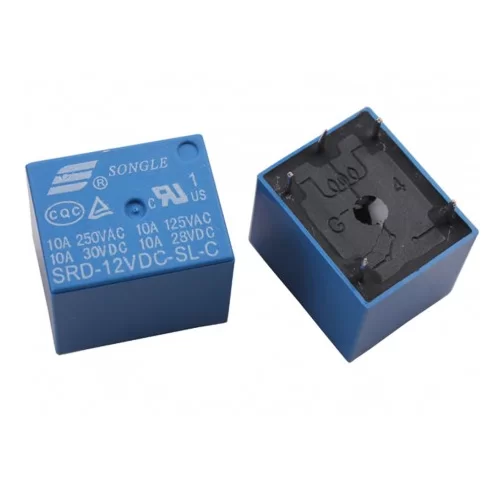
A 12V DC SPDT Power Relay is an electromechanical switch that uses a 12V DC power source to energize its coil, which in turn operates the switch contacts. The “SPDT” designation refers to its contact configuration: Single Pole, Double Throw. Let’s break down what this means:
Key Components and Functionality:
- Coil: A winding of wire that creates a magnetic field when a 12V DC current is applied to its terminals.
- Armature: A movable part that is attracted by the magnetic field generated by the coil.
- Contacts: The electrical switching elements. An SPDT relay has three contact terminals:
- Common (COM or C): This is the moving contact.
- Normally Closed (NC): When the coil is not energized, the common contact is connected to this terminal.
- Normally Open (NO): When the coil is energized, the common contact moves and connects to this terminal.
How it Works:
When 12V DC is applied to the relay’s coil terminals:
- The coil becomes energized, creating a magnetic field.
- This magnetic field attracts the armature.
- The movement of the armature causes the common (COM) contact to disconnect from the normally closed (NC) contact and connect to the normally open (NO) contact.
When the 12V DC power is removed from the coil:
- The magnetic field collapses.
- A spring (or other mechanism) returns the armature to its original position.
- The common (COM) contact disconnects from the normally open (NO) contact and reconnects to the normally closed (NC) contact.
Key Specifications to Consider:
- Coil Voltage: 12V DC (the voltage required to operate the relay).
- Contact Configuration: SPDT (Single Pole, Double Throw).
- Contact Rating (Voltage and Current): This specifies the maximum voltage and current that the relay contacts can safely switch. There will usually be separate ratings for AC and DC loads (e.g., 10A at 250VAC, 10A at 30VDC). It’s crucial not to exceed these ratings to prevent damage or failure. You might also see ratings for different load types (resistive vs. inductive).
- Coil Resistance: The resistance of the coil, which determines the current draw at the rated voltage (Ohm’s Law: I = V/R).
- Operating Time: The time it takes for the contacts to switch after the coil is energized.
- Release Time: The time it takes for the contacts to return to their normal state after the coil is de-energized.
- Mechanical Life: The number of switching cycles the relay can perform mechanically without electrical load.
- Electrical Life: The number of switching cycles the relay can perform under a specific electrical load. This is usually lower than the mechanical life and depends heavily on the load characteristics.
- Mounting Type: PCB mount, chassis mount, DIN rail mount, etc.
- Pin Configuration: The arrangement and number of pins for connecting the coil and contacts.
- Size and Package: The physical dimensions and type of enclosure.
- Operating Temperature: The range of ambient temperatures in which the relay can operate reliably.
Applications of 12V DC SPDT Power Relays:
SPDT relays are very versatile and used in a wide range of applications, including:
- Switching Power: Controlling higher power circuits (AC or DC) with a low-power 12V DC signal.
- Selecting Circuits: Choosing between two different circuits. For example, switching between a main power supply and a backup battery.
- Motor Control: Reversing the direction of DC motors (by switching the polarity of the voltage applied to the motor).
- Signal Routing: Directing signals to different paths.
- Automation Systems: Implementing logic and control in industrial and home automation.
- Automotive Applications: Controlling lights, horns, and other electrical components in vehicles.
- Interface Circuits: Isolating control circuits from the load circuits.
When choosing a 12V DC SPDT power relay, it’s crucial to consider:
- The voltage and current requirements of the load you need to switch. Ensure the relay’s contact rating meets or exceeds these requirements. Consider inrush currents for inductive loads.
- The voltage available to energize the relay coil (in this case, it must be 12V DC).
- The required switching speed and frequency.
- The expected lifespan and reliability needed for the application.
- The mounting requirements and physical size constraints.
- The operating environment (temperature, humidity, etc.).
By understanding these characteristics and specifications, you can select the appropriate 12V DC SPDT power relay for your specific application.
You must be logged in to post a review.









Reviews
There are no reviews yet.